When you’re choosing an oscilloscope, two terms you’ll often hear are bandwidth and sample rate. But what do these really mean for your measurements?
Understanding the difference between oscilloscope bandwidth and sample rate can make or break your ability to capture the signals you care about. If you want your oscilloscope to show you clear, accurate waveforms without missing critical details, you need to know how these two features work together.
Keep reading to discover how bandwidth and sample rate impact your oscilloscope’s performance—and how to choose the right balance for your needs.
Credit: www.ni.com
Oscilloscope Bandwidth Basics
An oscilloscope is a tool that shows electrical signals on a screen. Understanding its bandwidth helps you get clear and accurate signals. Bandwidth is one of the most important features of an oscilloscope. It tells you what range of signal frequencies the oscilloscope can measure well.
Knowing the basics of bandwidth helps you choose the right oscilloscope. It also ensures your measurements are correct. Below are key points about oscilloscope bandwidth and how it affects signal accuracy.
What Bandwidth Means
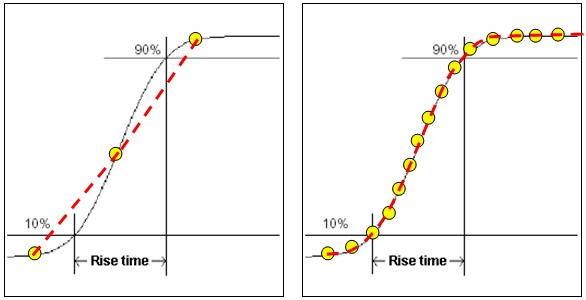
Bandwidth is the highest frequency an oscilloscope can capture accurately. Signals with frequencies above this limit appear weaker or distorted. Bandwidth is usually measured in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz).
For example, if an oscilloscope has a 100 MHz bandwidth, it can display signals up to 100 MHz clearly. Signals higher than this may lose detail or change shape on the screen.
Impact On Signal Accuracy
Low bandwidth can cause signals to look smaller or slower than they actually are. This leads to wrong readings and bad decisions. High bandwidth allows the oscilloscope to show more signal details.
Accurate signal display helps in detecting issues and understanding behavior. Without enough bandwidth, fast changes in signals may not appear correctly. This makes troubleshooting and analysis difficult.
Sample Rate Essentials
Understanding the sample rate is key to using an oscilloscope well. It shows how often the oscilloscope reads the signal each second. This affects how clear and detailed the signal appears on the screen. Choosing the right sample rate helps capture signals accurately without missing important details.
Defining Sample Rate
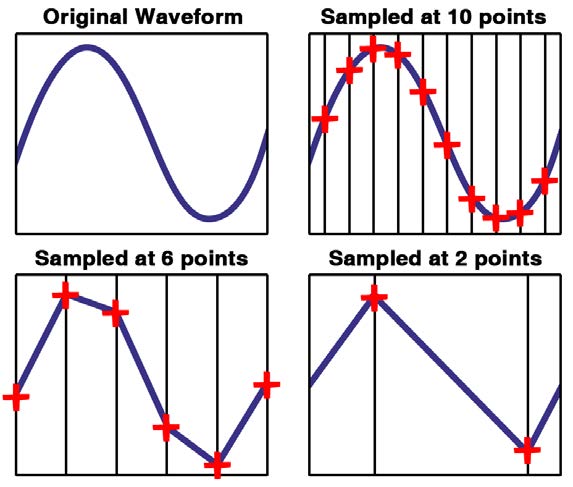
The sample rate measures how many times per second the oscilloscope records data points. It is usually shown in samples per second (S/s) or mega samples per second (MS/s). A higher sample rate means the oscilloscope takes more measurements in a given time. This helps in seeing fast changes in the signal clearly.
How Sample Rate Affects Data Capture
The sample rate controls the detail level in the captured signal. Too low a sample rate can miss quick signal changes. This leads to a wrong or unclear waveform display. A high sample rate captures more points and shows the waveform more accurately. It also reduces errors like aliasing, where the signal looks different than it really is.
Comparing Bandwidth And Sample Rate
Comparing bandwidth and sample rate helps us understand oscilloscope performance. Both affect how well an oscilloscope measures signals. These two specs serve different purposes but work together. Knowing their roles avoids measurement errors.
Role In Signal Measurement
Bandwidth defines the highest frequency the oscilloscope can measure accurately. It limits the range of signals you can see clearly. Sample rate is how often the oscilloscope takes data points per second. A higher sample rate captures more detail in the waveform. Bandwidth ensures signal clarity, while sample rate ensures signal detail.
Common Misconceptions
Many think higher sample rate means higher bandwidth. This is not true. You can have a fast sample rate but low bandwidth, causing distorted signals. Another mistake is assuming bandwidth alone shows signal quality. Both specs must match the signal needs for accurate results. Understanding their difference prevents wasted time and wrong readings.

Credit: www.allaboutcircuits.com
Choosing The Right Oscilloscope Specs
Choosing the right oscilloscope specs is key for accurate signal measurement. The right specs help capture signals clearly and avoid errors. Two main specs to consider are bandwidth and sample rate. Each affects how well the oscilloscope shows the signal details. Understanding these helps pick the best tool for your needs.
Matching Bandwidth To Application
Bandwidth limits the highest frequency an oscilloscope can measure. Signals with frequencies higher than the bandwidth will appear distorted. Choose bandwidth at least five times the highest signal frequency. This ensures the oscilloscope shows the signal shape correctly. For audio signals, lower bandwidth is fine. For fast digital signals, higher bandwidth is needed.
Selecting Optimal Sample Rate
Sample rate is how many times per second the oscilloscope records data points. A higher sample rate captures more detail in the signal. The rule of thumb is to use a sample rate at least ten times the bandwidth. This avoids missing important signal changes. Low sample rates cause signals to look blocky or wrong. Fast signals require faster sample rates for clear views.
Practical Effects On Waveform Display
Oscilloscope bandwidth and sample rate affect how waveforms appear on the screen. These two factors shape the details and accuracy of the signal you see. Understanding their practical effects helps in choosing the right oscilloscope for your needs.
Bandwidth Limitations In Action
Bandwidth controls the highest frequency the oscilloscope can show. If the signal frequency goes beyond this limit, the waveform looks distorted. Sharp edges become smooth, and fast changes can disappear.
This loss of detail can mislead your analysis. For example, a square wave may appear rounded. Bandwidth limits hide the true shape of the signal.
Sample Rate And Signal Resolution
Sample rate is how often the oscilloscope records data points. A low sample rate causes gaps between points. This makes the waveform look jagged or incomplete.
Higher sample rates capture more detail and create smoother waveforms. You can see small changes and fast events clearly. Without enough samples, important signal features may be missed.
Credit: www.nutsvolts.com
Advanced Considerations
Advanced considerations in oscilloscopes help users get the best results. Understanding the deeper link between bandwidth and sample rate is key. This knowledge helps analyze signals more accurately.
Interplay Between Bandwidth And Sample Rate
Bandwidth defines the range of frequencies the oscilloscope can measure. Sample rate shows how often the signal is recorded per second. Both must work together to capture signals correctly.
A high bandwidth with a low sample rate can miss important signal details. A high sample rate with low bandwidth might record noise or false data. Balancing these two ensures clear and reliable waveforms.
Impact On High-speed Signal Analysis
High-speed signals change very quickly over time. Without enough bandwidth, the oscilloscope cannot display these changes properly. Insufficient sample rate causes gaps in data, missing fast transitions.
Choosing the right bandwidth and sample rate helps catch every detail. This is vital for tasks like digital communication testing and fast pulse measurements. It prevents errors and improves the quality of signal analysis.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Oscilloscope Bandwidth And Why It Matters?
Oscilloscope bandwidth defines the highest frequency the device accurately measures. Higher bandwidth captures faster signals and details. It ensures precise waveform representation, critical for high-speed electronics testing and analysis.
How Does Sample Rate Affect Oscilloscope Performance?
Sample rate is how many data points per second the oscilloscope records. A higher sample rate improves signal resolution and detail. It prevents aliasing and captures rapid signal changes accurately.
Can Bandwidth And Sample Rate Be The Same?
No, bandwidth and sample rate differ in function. Bandwidth limits frequency measurement; sample rate controls data capture speed. Both are crucial but serve distinct roles in oscilloscope accuracy.
Why Choose Higher Bandwidth Over Sample Rate?
Higher bandwidth allows observing faster signal frequencies and transients. While sample rate affects data quality, bandwidth impacts signal range and clarity. Prioritize bandwidth for high-frequency signal analysis.
Conclusion
Choosing the right oscilloscope means knowing bandwidth and sample rate. Bandwidth shows how fast signals the scope can catch. Sample rate tells how many points it records each second. Both affect the quality of your signal view. A good balance helps you see clear and accurate waveforms.
Don’t just pick high numbers; match them to your needs. Understanding these basics makes using oscilloscopes easier and smarter. This helps you work better with electronic signals every day.

I’m Asif Ur Rahman Adib, an Electrical Engineer and lecturer. My journey began in the lab, watching students struggle with instruments they used every day without fully understanding them. Over time, I’ve combined teaching, research, and hands-on experience to help others grasp electrical concepts clearly, safely, and practically—whether it’s understanding a circuit or mastering a multimeter.