Are you trying to figure out whether a frequency counter or an oscilloscope is the right tool for your project? Both are powerful devices that measure electrical signals, but they serve very different purposes.
Choosing the wrong one could slow you down or lead to confusing results. You’ll discover exactly how each tool works, when you should use one over the other, and how making the right choice can save you time and effort.
Keep reading, and you’ll gain the confidence to pick the perfect instrument for your needs.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequency Counter Basics
The frequency counter is a tool used to measure how often a signal repeats. It helps to find the frequency of electronic signals. This tool is important for anyone working with radios, clocks, or other electronic devices. Understanding the basics of a frequency counter helps you know when and how to use it.
What It Measures
A frequency counter measures the number of cycles per second in a signal. This number is called frequency and is shown in hertz (Hz). It can measure very fast signals, from a few hertz to millions of hertz. The tool gives a clear number that shows how often a wave repeats.
Common Uses
Frequency counters are common in labs and workshops. They check radio signals to make sure they are correct. They help fix clocks and timers by measuring their signals. They are also used to test parts like oscillators and transmitters. This tool is useful for anyone working with electronic signals.
How It Works
The frequency counter counts the number of signal cycles in a set time. It uses an internal clock to measure this time precisely. Signals enter the device and create pulses for each cycle. The device counts these pulses and shows the result on a display. This method gives a fast and accurate frequency reading.
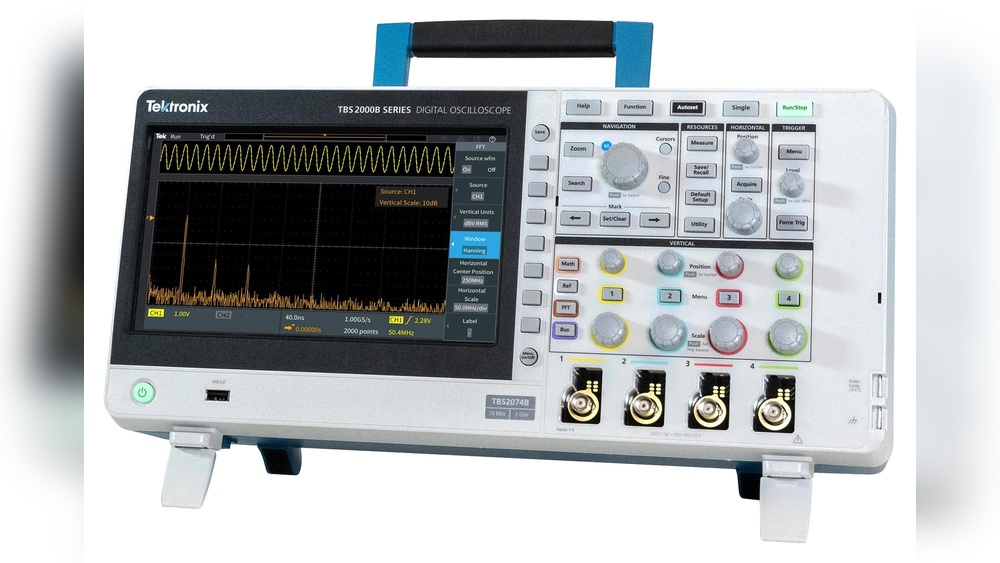
Oscilloscope Essentials
Understanding the basics of an oscilloscope is key to using it well. This tool helps you see electrical signals in real time. It shows how voltage changes over time on a screen. The oscilloscope turns invisible electrical waves into clear visuals.
It is not just about numbers. You get a picture of the signal’s shape and behavior. This helps spot problems and understand circuits better. Let’s explore the core features that make oscilloscopes essential.
Waveform Visualization
The oscilloscope displays waveforms as graphs. The horizontal axis shows time, the vertical shows voltage. This lets you watch signals move and change. You can see pulses, waves, and noise clearly. It makes complex signals easier to study and fix.
Typical Applications
Oscilloscopes have many uses in electronics and science. Engineers use them to test circuits and devices. Technicians find faults in wires and components. They also check signal timing and strength. In education, they teach students about wave behavior. Medical fields use them for monitoring heartbeats and brain waves.
Operating Principles
An oscilloscope works by capturing voltage signals from a probe. It converts these signals into a visible graph on the screen. Inside, it uses an electron beam or digital sampling to plot data points. The device updates this display many times per second. This rapid refresh makes motion and changes easy to watch.
Measurement Capabilities
Measurement capabilities define the core difference between frequency counters and oscilloscopes. Each tool offers unique ways to analyze electronic signals. Understanding these capabilities helps choose the right device for your needs.
Frequency counters and oscilloscopes measure signals but focus on different aspects. Frequency counters excel in counting signal cycles per second. Oscilloscopes display waveforms and provide detailed signal information over time.
Frequency Detection
Frequency counters measure signal frequency with high precision. They count the number of cycles in a set time. This makes them ideal for stable signals with a steady frequency. Oscilloscopes can also detect frequency but less accurately. They show frequency visually by displaying wave patterns.
Signal Amplitude
Oscilloscopes measure signal amplitude effectively. They display voltage changes over time as waveforms. This helps observe signal strength and variations. Frequency counters do not measure amplitude. They focus solely on counting cycles without showing voltage levels.
Time Domain Analysis
Oscilloscopes provide detailed time domain analysis. They show how signals change over microseconds or milliseconds. This helps identify signal distortions and noise. Frequency counters lack this feature. They only count frequencies without showing signal behavior over time.

Credit: www.keysight.com
Accuracy And Precision
Accuracy and precision are key in measuring electrical signals. Accuracy shows how close a reading is to the true value. Precision shows how consistent measurements are over time. Both matter for reliable results. Different tools offer different levels of accuracy and precision. Understanding these differences helps you choose the right device.
Frequency Counter Accuracy
Frequency counters give very accurate measurements. They count cycles of a signal in a set time. Their accuracy depends on the internal clock. A stable clock means fewer errors. Some models have accuracy up to parts per million. This suits tasks needing exact frequency data. But counters may struggle with very low or noisy signals.
Oscilloscope Precision
Oscilloscopes show signal shape and timing. They offer high precision in time and voltage. Precision means small changes are visible. This helps analyze signal quality and disturbances. Digital oscilloscopes sample signals rapidly. This gives detailed views of waveforms. But their accuracy depends on calibration and settings.
Factors Affecting Results
Several factors affect accuracy and precision. Signal strength and noise can cause errors. Device quality and calibration are vital. User skill in setup also matters. Environmental conditions like temperature can change readings. Understanding these helps improve measurement reliability.
User Interface And Ease
User interface and ease of use are key factors when choosing between a frequency counter and an oscilloscope. Both tools serve different purposes but their design affects how quickly users can start working. Clear displays, intuitive controls, and simple setup can save time. Understanding data easily also helps in making faster decisions.
Display And Controls
Frequency counters usually have a straightforward digital display. Numbers show frequency clearly and without clutter. Controls are minimal, often just a few buttons or knobs. This makes it simple for beginners to operate.
Oscilloscopes have larger screens with more detail. They show waveforms graphically, which can be complex. Controls include multiple buttons, knobs, and menus. This allows more functions but may confuse new users.
Setup Complexity
Setting up a frequency counter is quick. Connect the signal and power it on. Few settings need adjusting. This ease suits quick tests or basic measurements.
Oscilloscopes require more setup. Users must select channels, adjust scales, and set triggers. These steps need more time and knowledge. It suits detailed analysis rather than simple checks.
Data Interpretation
Frequency counters display numbers directly, making results easy to read. Users do not need to interpret graphs or signals. This clarity helps in straightforward measurements.
Oscilloscopes provide detailed waveforms. Users must understand signal shapes and timing. This allows deeper insight but needs more skill. It is useful for troubleshooting and advanced study.
Credit: yourpghlawyer.com
Applications Comparison
Frequency counters and oscilloscopes serve different roles in electronics testing. Each tool fits specific tasks better. Understanding their applications helps pick the right device for your needs.
Both instruments measure electrical signals but show different details. Frequency counters give precise frequency values. Oscilloscopes display signal shape and changes over time.
When To Use Frequency Counters
Use frequency counters to measure exact frequencies of signals. Ideal for radio transmitters, clocks, and signal generators. They work best when you need precise frequency data fast. Simple signals with steady frequency suit counters perfectly.
When To Use Oscilloscopes
Oscilloscopes show signal waveforms and timing details. Use them to analyze complex or changing signals. Good for troubleshooting circuits and viewing signal distortions. They help detect noise, glitches, and timing errors visually.
Industry Preferences
Radio and communication industries prefer frequency counters for tuning and testing. Electronics design and repair sectors favor oscilloscopes for detailed signal analysis. Both tools often work together for full signal assessment.
Cost And Portability
Cost and portability are important factors when choosing between a frequency counter and an oscilloscope. Both tools serve different purposes but vary greatly in price and ease of transport. Understanding these differences helps you pick the best device for your needs.
Price Range
Frequency counters are usually less expensive than oscilloscopes. Basic models can cost under $100. More advanced frequency counters might reach a few hundred dollars. Oscilloscopes tend to start at a higher price point. Entry-level digital oscilloscopes often cost several hundred dollars. High-end models with more features can run into thousands. Budget plays a big role in your choice.
Size And Portability
Frequency counters are compact and lightweight. Many handheld models fit easily in a pocket or bag. This makes them ideal for fieldwork and quick checks. Oscilloscopes are larger and heavier. Bench-top models need stable surfaces and space. Portable oscilloscopes exist but still weigh more than frequency counters. Portability is key for users on the move.
Maintenance Needs
Frequency counters require minimal maintenance. They are simple devices with fewer parts. Battery replacement and occasional calibration are usually enough. Oscilloscopes need more care. They have complex circuits and screens. Regular calibration and careful handling extend their life. Maintenance costs are higher for oscilloscopes. Consider this before making a purchase.
Choosing The Right Tool
Choosing the right tool between a frequency counter and an oscilloscope depends on what you need to measure. Each device offers unique features that fit different tasks. Understanding your main requirements helps pick the best option.
Based On Measurement Needs
Frequency counters measure signal frequency accurately and quickly. They are perfect for simple tasks like counting pulses or checking clock speeds. Oscilloscopes show signal waveforms, allowing detailed analysis of signal shape and timing. Use an oscilloscope when you need to see how signals change over time.
Budget Considerations
Frequency counters usually cost less than oscilloscopes. They suit users with smaller budgets or those needing basic measurements. Oscilloscopes can be expensive but offer more functions. Consider your budget carefully before choosing a tool.
Future Proofing
Think about your future projects and needs. Oscilloscopes provide more flexibility for complex tasks and new technologies. Frequency counters may limit your options later. Choosing a device that adapts to future demands saves money and effort over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Main Difference Between Frequency Counter And Oscilloscope?
A frequency counter measures signal frequency precisely. An oscilloscope visually displays waveform shape, amplitude, and timing. Frequency counters focus on numerical accuracy, while oscilloscopes provide detailed signal analysis with graphical output.
When Should I Use A Frequency Counter Over An Oscilloscope?
Use a frequency counter for quick, accurate frequency measurements. Choose an oscilloscope when you need to analyze waveform shape, timing, or signal integrity in detail.
Can An Oscilloscope Measure Frequency Accurately Like A Frequency Counter?
Oscilloscopes can estimate frequency but with less precision than frequency counters. Frequency counters are specialized for exact frequency readings, especially for stable signals.
What Are The Key Applications Of Frequency Counters And Oscilloscopes?
Frequency counters are ideal for radio, communication, and signal testing. Oscilloscopes suit troubleshooting, waveform analysis, electronic design, and time-domain signal examination.
Conclusion
Choosing between a frequency counter and an oscilloscope depends on your needs. Frequency counters measure signal frequency quickly and accurately. Oscilloscopes show signal shape and changes over time. Both tools have clear strengths. For simple frequency checks, a frequency counter works well.
For detailed signal analysis, an oscilloscope is better. Understanding what each device does helps you pick the right one. Use the right tool to get the best results in your work. Simple tools for simple tasks. Complex tools for complex signals.

I’m Asif Ur Rahman Adib, an Electrical Engineer and lecturer. My journey began in the lab, watching students struggle with instruments they used every day without fully understanding them. Over time, I’ve combined teaching, research, and hands-on experience to help others grasp electrical concepts clearly, safely, and practically—whether it’s understanding a circuit or mastering a multimeter.