Are you confused about choosing between a high impedance and a low impedance multimeter? Understanding the difference can save you time, protect your devices, and give you more accurate readings.
Whether you’re a hobbyist or a professional, knowing which multimeter suits your needs is crucial. This article will clear up the mystery, help you avoid costly mistakes, and empower you to make smarter decisions every time you test a circuit.
Keep reading to find out exactly how these two types differ and which one is right for you.
Credit: www.allaboutcircuits.com
What Is Impedance In Multimeters
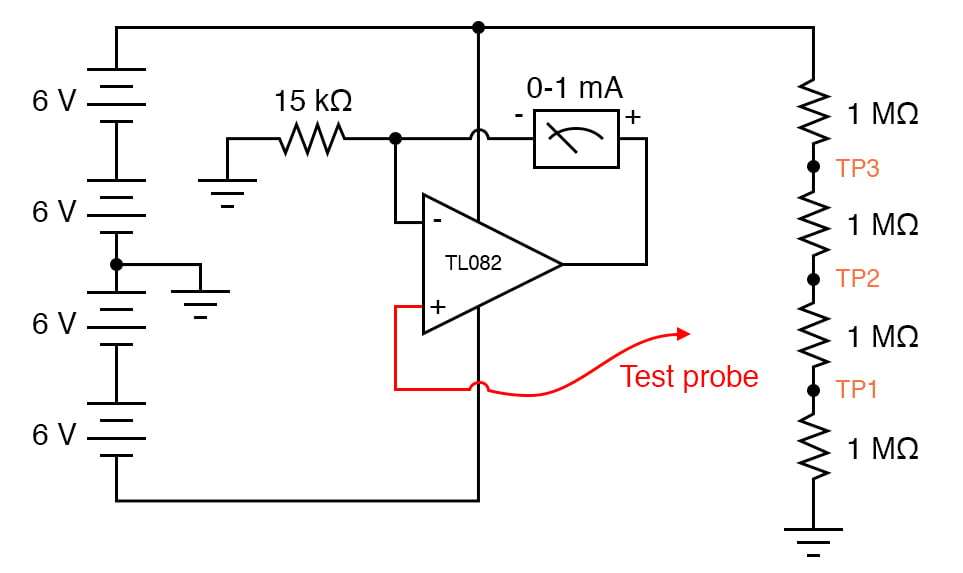
Impedance in multimeters is an important concept that affects measurement accuracy. It refers to how much a multimeter resists the flow of electric current. This resistance changes depending on the multimeter’s design and function. Understanding impedance helps users pick the right tool for their tasks.
Different multimeters have different impedance levels. High impedance multimeters draw very little current from the circuit. Low impedance multimeters draw more current. This difference impacts how the multimeter interacts with the circuit being tested.
What Does Impedance Mean In Multimeters?
Impedance is a measure of resistance in electrical circuits. It includes both resistance and reactance. Reactance comes from capacitors and inductors in the circuit. High impedance means the multimeter resists current flow strongly. Low impedance means less resistance to current flow.
Why Is Impedance Important?
Impedance affects the accuracy of voltage and current readings. High impedance multimeters cause minimal circuit disturbance. They do not change the circuit’s behavior during measurement. Low impedance multimeters may affect the circuit and give different readings.
How Does Impedance Affect Measurements?
High impedance meters prevent current from flowing into the meter. This keeps the circuit stable. Low impedance meters allow more current to flow. This can lead to incorrect voltage readings. Choosing the right impedance avoids errors and protects sensitive components.
Credit: www.toacanada.com
Characteristics Of High Impedance Multimeters
High impedance multimeters have a unique set of traits. They measure electrical signals without changing the circuit. Their high resistance stops current flow from the meter into the circuit. This feature protects sensitive devices and provides accurate readings.
These meters show minimal effect on the circuit under test. They are ideal for measuring voltages in delicate electronics. Their design reduces the chance of errors caused by the meter itself.
How High Impedance Affects Measurements
High impedance means the meter draws very little current. This prevents the meter from altering the circuit voltage. It helps get true voltage readings in sensitive parts. The meter acts like a gentle observer rather than a participant.
This trait reduces load on the circuit. It also avoids damage to small components. The meter can measure voltage without disturbing the signal. This leads to more reliable and stable measurements.
Common Uses For High Impedance Multimeters
High impedance meters are common in electronics repair and testing. They suit circuits with tiny currents and voltages. Engineers use them to check sensors and microchips. They also work well for audio and radio equipment.
These meters are perfect for troubleshooting circuits with sensitive parts. They help find faults without causing more problems. Their gentle measurement style makes them a standard tool for fine electronics work.
Features Of Low Impedance Multimeters
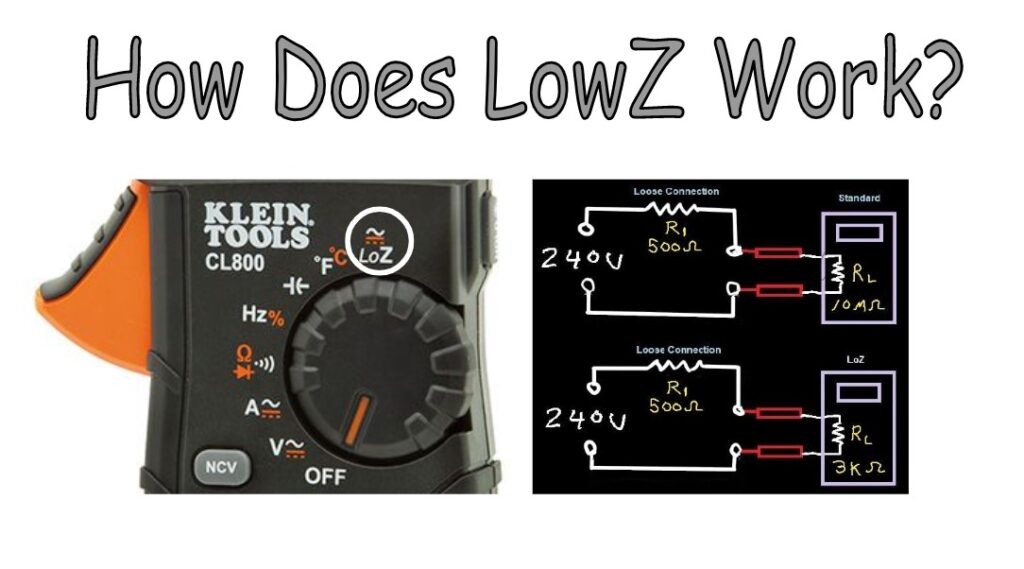
Low impedance multimeters have unique features that set them apart from standard meters. They measure voltage and current with low internal resistance. This helps avoid false readings caused by stray currents. These meters are designed to provide accurate results in complex circuits.
They also reduce the chance of ghost voltages. Ghost voltages appear due to electrical noise or capacitive coupling. Low impedance multimeters eliminate these by drawing more current during measurement. This makes them reliable tools for electricians and technicians.
Impact On Circuit Testing
Low impedance multimeters affect circuit testing by giving clear, stable readings. They prevent false voltage signals that can confuse testers. This helps find real issues faster and saves time. They also protect sensitive components by applying a low resistance load. This avoids damage during measurement.
Typical Applications For Low Impedance
These meters are common in electrical troubleshooting and maintenance. They work well in residential and commercial wiring checks. They help test lighting circuits and detect wiring errors. Low impedance meters are useful in automotive repairs and appliance testing too. Their ability to ignore ghost voltages makes them ideal for any noisy electrical environment.
Comparing Accuracy And Sensitivity
Accuracy and sensitivity are key factors in choosing a multimeter. They affect how well the device measures electrical signals. High impedance and low impedance multimeters differ in these areas.
Understanding these differences helps pick the right tool for your needs. Both types have strengths and weaknesses in accuracy and sensitivity.
Accuracy In High Impedance Multimeters
High impedance multimeters draw very little current from the circuit. This means they do not affect the circuit’s operation much. They provide precise voltage readings without altering the signal.
This accuracy is important for sensitive electronics. It helps avoid damage and incorrect measurements. High impedance meters are best for measuring voltage in delicate circuits.
Accuracy In Low Impedance Multimeters
Low impedance multimeters draw more current from the circuit. This can load the circuit and change the voltage slightly. It may reduce measurement accuracy in some cases.
Despite this, low impedance meters are accurate for many general tasks. They work well for testing batteries, motors, and other robust components.
Sensitivity Differences Between High And Low Impedance
Sensitivity means detecting small changes in electrical signals. High impedance meters are very sensitive to tiny voltage variations. They can detect weak signals without interference.
Low impedance meters are less sensitive to small signals. They are designed to handle stronger signals and avoid false readings caused by noise.
Safety Considerations For Both Types
Safety is key when using any multimeter. Both high impedance and low impedance meters have risks. Understanding these helps prevent accidents and damage.
Choosing the right meter for the job protects you and your devices. Each type needs careful handling to ensure safe measurements.
Safety Tips For High Impedance Multimeters
High impedance meters protect circuits by drawing very little current. This reduces the chance of circuit damage. Still, avoid measuring high voltages beyond the meter’s rating. Always check the meter’s category rating before use. Use insulated probes and keep your hands dry. Never touch the metal parts during testing. Disconnect power sources before testing resistance or continuity. Store the meter in a safe, dry place.
Safety Tips For Low Impedance Multimeters
Low impedance meters help avoid false readings due to ghost voltages. They draw more current, so use caution to avoid shorts. Check the maximum input limits on your meter. Do not measure live circuits beyond these limits. Use proper personal protective equipment like gloves and goggles. Keep probes steady and avoid contact with other components. Turn off the circuit power when possible before testing. Handle the meter and leads gently to prevent damage.
Credit: techcircuit.org
Choosing The Right Multimeter For Your Needs
Choosing the right multimeter is essential for accurate measurements and safe work. The choice depends on your specific needs and the tasks you perform. Understanding the difference between high impedance and low impedance multimeters helps you pick the best tool. This guide breaks down important factors and typical uses for each type.
Factors To Consider Before Buying
First, think about what you will measure most often. High impedance multimeters draw less current from the circuit. This avoids affecting sensitive electronics or low-power devices. Low impedance meters can handle heavy loads and noisy signals better. They often filter out false readings caused by stray voltages.
Next, check your budget and quality needs. High impedance meters tend to cost more but offer precision. Low impedance meters are usually simpler and less expensive. Consider the meter’s durability and battery life for fieldwork. Also, look for safety ratings suitable for your work environment.
Situations Favoring High Or Low Impedance
Use a high impedance multimeter for testing circuits with delicate components. It prevents damage and gives accurate voltage readings. Ideal for electronics repair, research, and small signal measurements. It works well with sensors, microcontrollers, and digital circuits.
Choose a low impedance multimeter in environments with electrical noise or ghost voltages. It helps get true readings by blocking interference. Useful for automotive diagnostics, industrial equipment, and house wiring checks. It also protects against false signals in energized circuits.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between High And Low Impedance Multimeters?
High impedance multimeters have input resistance above 10 MΩ, minimizing circuit load. Low impedance meters typically have 10 kΩ to 1 MΩ, causing more circuit loading and interference.
When Should I Use A High Impedance Multimeter?
Use high impedance meters to measure sensitive or low-current circuits. They prevent circuit disturbance and provide more accurate voltage readings in delicate electronics.
Are Low Impedance Multimeters Better For Noisy Environments?
Yes, low impedance multimeters reduce false readings from stray voltages in noisy or ghost voltage environments. They are ideal for troubleshooting electrical wiring issues.
Does High Impedance Affect Measurement Accuracy?
High impedance improves measurement accuracy by minimizing the meter’s impact on the circuit. It prevents voltage drops across internal resistance during testing.
Conclusion
Choosing between high impedance and low impedance multimeters depends on your needs. High impedance meters protect sensitive circuits from damage. Low impedance meters help avoid false readings from ghost voltages. Knowing these differences helps you pick the right tool. This choice improves accuracy and safety in measurements.
Always match your multimeter type to the task at hand. Simple understanding leads to better results and fewer errors. Keep your work safe and precise with the correct multimeter.

I’m Asif Ur Rahman Adib, an Electrical Engineer and lecturer. My journey began in the lab, watching students struggle with instruments they used every day without fully understanding them. Over time, I’ve combined teaching, research, and hands-on experience to help others grasp electrical concepts clearly, safely, and practically—whether it’s understanding a circuit or mastering a multimeter.



