Are you confused about the difference between a vectorscope and an oscilloscope? You’re not alone.
Both tools look similar and deal with signals, but they serve very different purposes. Understanding how each one works can save you time, improve your projects, and make your work with electronics or video signals much easier. Keep reading, and you’ll quickly discover which tool fits your needs and why it matters for your next project.
Don’t miss out on the key details that could change the way you handle signal analysis forever.
Purpose And Use
The purpose and use of vectorscopes and oscilloscopes differ greatly. Each device serves unique roles in electronics and video signal analysis. Understanding their functions helps choose the right tool for specific tasks. Both tools display waveforms but focus on different signal characteristics.
Functions Of A Vectorscope
A vectorscope measures and displays color information in video signals. It shows the hue and saturation of colors on a circular graph. This helps video engineers check if colors are accurate and balanced. The vectorscope also identifies color shifts or distortions in broadcasts or recordings. It is essential for color grading and video calibration.
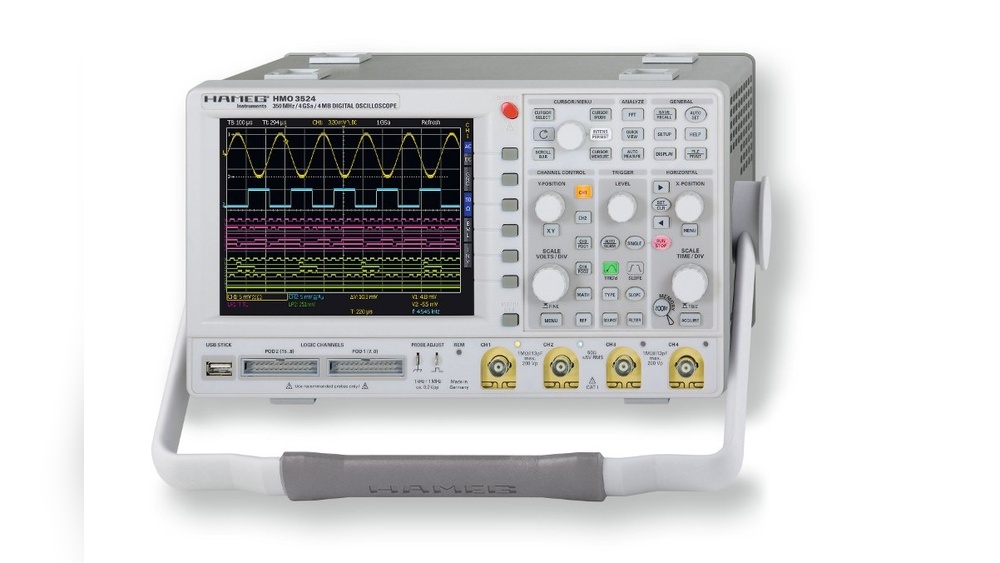
Functions Of An Oscilloscope
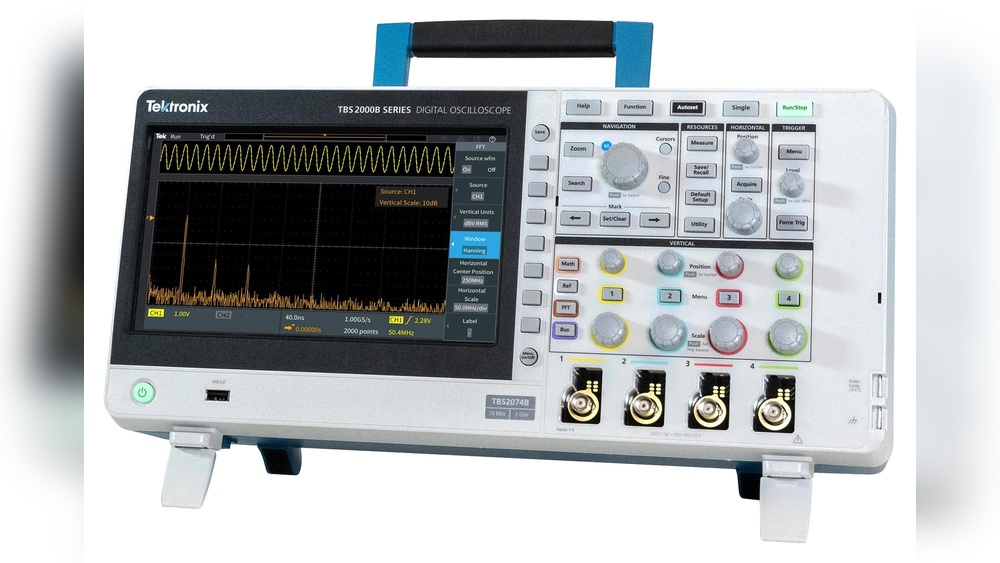
An oscilloscope displays electrical signals as waveforms over time. It shows voltage changes and signal patterns clearly. This helps technicians observe signal behavior and detect faults. Oscilloscopes measure frequency, amplitude, and timing of signals. They are widely used in electronics design, testing, and repair.
Typical Applications
Vectorscopes are common in TV studios and video production. They ensure proper color reproduction and signal quality. Oscilloscopes are found in laboratories, factories, and repair shops. Engineers use them to test circuits, troubleshoot devices, and analyze signals. Both tools improve the accuracy and reliability of electronic and video systems.

Credit: forums.arcade-museum.com
Signal Display Techniques
Signal display techniques show how electronic signals appear visually. These methods help users understand and analyze signal properties. Vectorscopes and oscilloscopes use different ways to display signals. Each technique offers unique views of signal behavior.
Color Signal Representation
Vectorscopes display color signals by showing their hue and saturation. They plot colors on a circular graph. This graph maps the color’s angle and strength. It helps in checking color accuracy and balance. Users can see if colors match broadcast standards.
Vectorscopes do not show brightness or luminance. They focus on the color information only. This makes them ideal for color correction tasks. Users can quickly spot color shifts or errors.
Waveform Visualization
Oscilloscopes show waveforms as lines on a grid screen. These lines represent voltage over time. This view helps users see signal shape, timing, and strength. It reveals noise, distortion, or interruptions in the signal.
Waveform visualization shows brightness, contrast, and sync signals. It helps in troubleshooting and adjusting video or audio signals. Users can analyze detailed signal changes frame by frame.
Measurement Parameters
Measurement parameters define what each device can analyze and display. Both vectorscopes and oscilloscopes serve unique roles in electronics and video signal analysis. Understanding their key measurement parameters helps choose the right tool for your needs.
Color Accuracy And Saturation
Vectorscopes focus on color information in video signals. They measure hue and saturation accurately. Hue shows the color shade, while saturation shows color intensity.
These measurements help video professionals maintain color consistency. The vectorscope displays color points on a circular graph. This visual helps spot color shifts or errors quickly. It is essential for color correction and broadcast quality control.
Voltage And Time Measurements
Oscilloscopes measure voltage changes over time. They provide a waveform display of electrical signals. This helps users analyze signal shape, frequency, and amplitude.
Oscilloscopes are critical for diagnosing electronic circuits. They show how voltage varies with time in a clear graph. This allows detection of faults like noise, spikes, or timing issues. The device can also measure pulse width and signal delay accurately.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Device Design And Components
The design and components of vectorscopes and oscilloscopes reflect their unique roles in signal analysis. Both devices capture and display electrical signals, but their hardware suits different tasks. Understanding their design helps users choose the right tool for their needs.
Vectorscope Hardware Features
Vectorscopes focus on color and phase analysis in video signals. They include a cathode ray tube or LCD screen to show color vectors. A key part is the color decoder, which separates signals into color components. This device uses a phase detector to measure hue and saturation. The input stage is designed for video signals, often supporting composite or component formats. Its controls allow adjustment of signal gain and phase for precise color measurement.
Oscilloscope Hardware Features
Oscilloscopes display voltage changes over time on a screen. They have vertical and horizontal amplifiers to control signal display. The vertical amplifier adjusts signal size, while the horizontal amplifier controls time base. A trigger circuit stabilizes repeating waveforms for clear viewing. Inputs include probes that connect to various signal types. Modern oscilloscopes often include digital converters for signal processing and storage. The user interface offers controls for scale, time, and trigger settings.
Usage In Different Industries
Vectorscopes and oscilloscopes serve different roles across industries. Each tool fits specific tasks based on the needs of the field. Understanding their uses helps choose the right one for the job. Below, explore their applications in key industries.
Broadcast And Video Production
Vectorscopes play a vital role in video production. They measure color information in video signals. This tool ensures accurate color balance and quality. Broadcast engineers rely on vectorscopes to maintain consistent visuals.
Using a vectorscope, professionals check hues and saturation. It helps detect color errors before broadcast. This prevents poor picture quality on TV screens. The vectorscope’s display shows color shifts clearly.
Electronics And Engineering
Oscilloscopes are essential in electronics and engineering fields. They visualize electrical signals as waveforms on a screen. Engineers analyze signal timing, voltage, and noise with oscilloscopes. This aids in circuit design and troubleshooting.
Oscilloscopes help detect faults in devices and systems. They show signal changes over time, offering detailed insights. This tool is critical for testing and development tasks. Engineers trust oscilloscopes for precise measurements.
Interpreting The Output
Understanding the output of a vectorscope and an oscilloscope is key to using them well. Both tools show different types of signals. Each output needs a specific way to read and analyze. This helps in making the right decisions based on what the instruments display.
Reading Vectorscope Patterns
A vectorscope shows color information as shapes on a circular graph. Each shape tells you about the color’s hue and saturation. A tight, small shape means low saturation. A large, spread-out shape means high saturation. The shape’s position shows the hue angle. Centered patterns mean little or no color. Patterns that stretch out show strong colors. Watching these shapes helps adjust color balance and correct video signals.
Analyzing Oscilloscope Waveforms
An oscilloscope displays voltage signals as waveforms over time. The horizontal axis shows time. The vertical axis shows signal strength. Regular wave shapes mean stable signals. Irregular or noisy waves suggest problems. The height shows signal amplitude. The width shows signal duration. Sharp edges or spikes may indicate interference. Watching these waveforms helps find and fix electrical issues quickly.
Advantages And Limitations
Understanding the advantages and limitations of vectorscopes and oscilloscopes helps choose the right tool. Each device serves a specific purpose in signal analysis. Knowing their strengths and weaknesses improves your work accuracy and efficiency.
Strengths Of Vectorscopes
Vectorscopes excel at displaying color information in video signals. They show hue and saturation clearly. This makes color correction easier and faster. Vectorscopes provide a visual map of color balance. They help detect color shifts and errors quickly. Their interface is simple and focused on color data.
Strengths Of Oscilloscopes
Oscilloscopes measure voltage changes over time. They reveal waveform shapes and signal timing. This helps diagnose electrical issues and test circuits. Oscilloscopes work well with many signal types. They offer detailed views of complex waveforms. This tool is essential for hardware troubleshooting.
Common Limitations
Neither vectorscopes nor oscilloscopes show all signal details. Vectorscopes cannot display signal timing or waveform shape. Oscilloscopes do not provide clear color information. Both devices require some training to use effectively. They can be expensive for casual users. Each tool fits specific tasks, not all situations.
Choosing The Right Tool
Choosing the right tool between a vectorscope and an oscilloscope depends on your needs. Each device serves a different purpose in signal analysis. Picking the right one helps you get accurate results fast. Understanding their differences is key to making the best choice.
Factors To Consider
Think about the type of signals you will analyze. A vectorscope shows color information in video signals. An oscilloscope displays electrical waveforms over time. Consider the complexity of the signal and the level of detail needed.
Also, check the ease of use. Vectorscopes have simpler displays for color checks. Oscilloscopes offer more detailed views but need more skill. Budget and availability matter too. Choose a tool that fits your resources and skill level.
Use Case Scenarios
Use a vectorscope for video production and color grading tasks. It helps ensure accurate color balance and signal quality. An oscilloscope suits electronics and engineering work. It shows voltage changes, wave shapes, and timing.
For troubleshooting circuits, oscilloscopes are the preferred choice. For broadcast or film color work, vectorscopes provide clear insights. Match the tool to your specific job for better results and efficiency.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Main Difference Between Vectorscope And Oscilloscope?
A vectorscope displays color information in video signals, while an oscilloscope measures electrical waveforms. Vectorscopes help in color grading, and oscilloscopes analyze voltage changes over time.
How Does A Vectorscope Help In Video Editing?
Vectorscopes visualize color hue and saturation, aiding precise color correction. They ensure color balance and consistency across video footage for professional results.
Can An Oscilloscope Display Color Signals Like A Vectorscope?
No, oscilloscopes show voltage versus time waveforms, not color data. They are used for electrical signal analysis, unlike vectorscopes specialized in color video signals.
Which Device Is Better For Signal Analysis: Vectorscope Or Oscilloscope?
It depends on the signal type. Use a vectorscope for video color signals and an oscilloscope for electrical waveform measurements.
Conclusion
Both vectorscopes and oscilloscopes help analyze signals clearly. Vectorscopes focus on color and phase in video signals. Oscilloscopes show voltage changes over time for many signals. Choosing the right tool depends on your specific needs. Each device offers unique views of electronic data.
Understanding their differences makes your work easier. Use this knowledge to pick the best tool. Signal testing becomes simpler with the right choice. Keep exploring to improve your electronics skills.

I’m Asif Ur Rahman Adib, an Electrical Engineer and lecturer. My journey began in the lab, watching students struggle with instruments they used every day without fully understanding them. Over time, I’ve combined teaching, research, and hands-on experience to help others grasp electrical concepts clearly, safely, and practically—whether it’s understanding a circuit or mastering a multimeter.